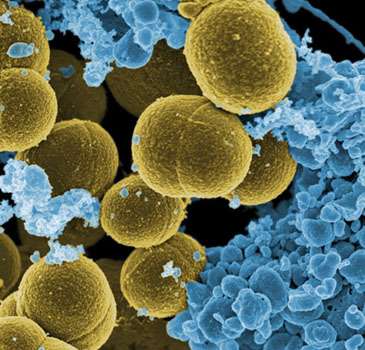
Staphylococcus Aureus
• Staphylococcus aureus is the leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections such as abscesses, furuncles, and cellulitis.
• It is a type of bacteria that about 30% of people carry in their noses.
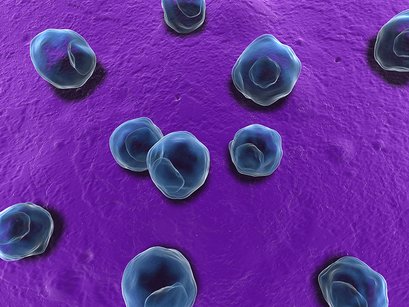
Chlamydia Pneumoniae
• Chlamydia pneumoniae is a type of bacteria that can cause lung infections, such as pneumonia.

Mycoplasma Pneumoniae
• Mycoplasma pneumoniae is a common cause of upper respiratory tract infection, and remains the most common cause of bacterial pneumonia.
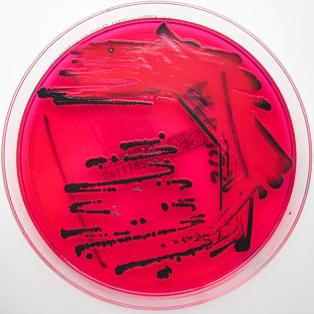
Salmonella sp.
• Salmonella sp. are a group of bacteria which reside in the intestinal tract of human beings and are capable of causing disease.
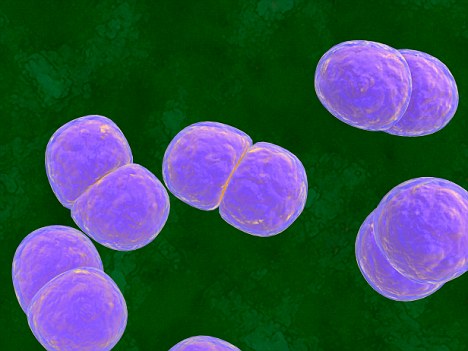
Moraxella Catarrhalis
• Moraxella catarrhalis is a fastidious, nonmotile, Gram-negative, aerobic, oxidase-positive diplococcus that can cause infections of the respiratory system, middle ear, eye, central nervous system, and joints of humans.
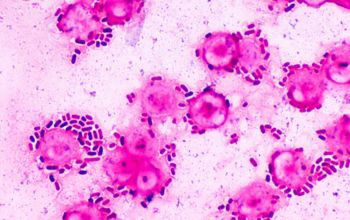
Klebsiella Pneumoniae
• Klebsiella pneumoniae is a common enterobacterium that causes a disease spectrum that includes severe pneumonia, enteritis, urinary tract infection, and miscellaneous septic lesions, including sinusitis, meningitis, and otitis.
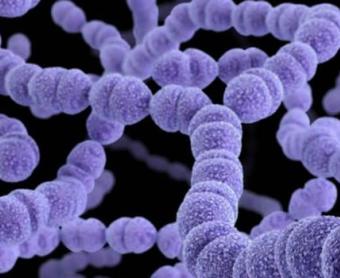
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
• Streptococcus pneumoniae is a bacterium that commonly causes ear infections in children.
• It also is the most common cause of community-acquired pneumonia, sinus infections and “pink-eye.”
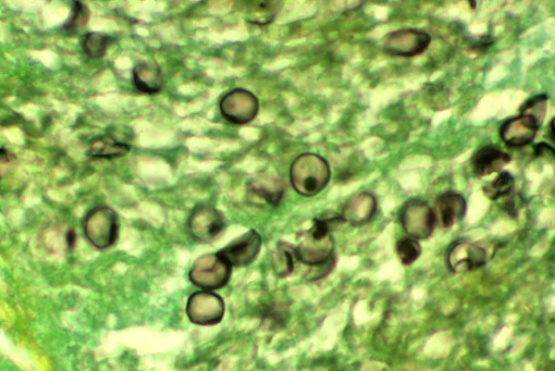
Pneumocystis Jirovecii
• Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is a fungal infection of the lungs.
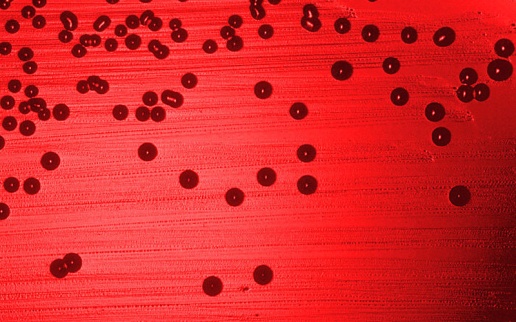
Haemophilus Influenzae
• Haemophilus influenzae disease refers to any infection caused by H. influenzae bacteria.
Legionella Pneumophila
• Legionnaires' disease is a severe infection caused by Legionella species, primarily L. pneumophila. In fact, L. pneumophila is responsible for 90% of infections.
• The disease typically presents as pneumonia and symptoms may include a high fever, chills, cough, muscle aches, headaches, and diarrhea.